The concepts of state and government are fundamental to political science, yet they are often used interchangeably in everyday discourse. In academic literature, however, these terms represent distinct and analytically separable entities.
The State
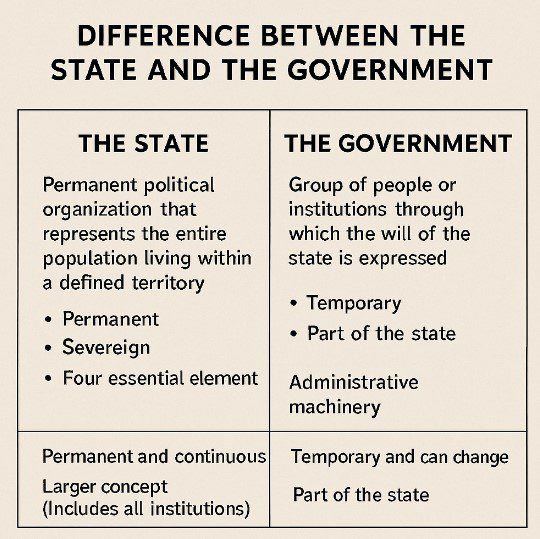
The state is a permanent and sovereign political organization that encompasses the totality of institutions responsible for maintaining order, enforcing laws, and representing collective authority. It consists of four essential elements: population, defined territory, governmental institutions, and sovereignty. The state is characterized by continuity and permanence; it persists regardless of changes in leadership or political administration. Moreover, it includes a wide range of institutions—such as the legislature, executive, judiciary, bureaucracy, and security apparatus—that collectively uphold the legal and political framework of the society. In this sense, the state represents the enduring structure of political authority.
The Government
In contrast, the government refers to the group of individuals and agencies that are temporarily entrusted with the authority to make decisions and implement policies on behalf of the state. It is essentially the operational or administrative arm of the state. Governments are transitory and change periodically, typically through electoral processes, legal transitions, or political shifts. Unlike the state, which is an abstract and comprehensive entity, the government is concrete and specific, representing the leadership currently exercising power.
Key Distinctions
The state is broader, continuous, and institutional, whereas the government is narrower, temporary, and changeable. The state embodies sovereign authority and the long-term political order, while the government constitutes the temporary managers or agents who act within that order. Philosophers such as Max Weber emphasize that the state holds the legitimate monopoly of force, whereas the government merely administers this authority.
Concise Comparative Summary
| State | Government |
|---|---|
| Permanent, continuous, and sovereign entity | Temporary body of individuals in power |
| Composed of institutions such as the judiciary, the legislature, the bureaucracy, and the security forces | Only the executive and administrative leadership |
| Exists independently of any particular ruling group | Changes through elections or political transitions |
| Represents the long-term structure of political authority | Represents current political leadership and policymaking |
Stay tuned with Societypedia.com for more!